House_of_Orange是来自Hitcon CTF 2016中的一道同名题目,是一种通过unstoredbin attack修改_IO_list_all指针,伪造_IO_FILE_plus结构体和vtable虚表,进而修改虚表函数劫持控制流的方法,glibc在2.24版本后加入了对虚表的验证,这题用的glibc版本是2.23,还没有虚表相关的安全检查。
网上关于House of Orange的资料有很多,我就从另一个角度来讲一下我遇到的问题和知识点。
0x00 FILE、_IO_FILE、_IO_FILE_plus、_IO_list_all、vtable是什么
FILE 在 Linux 系统的标准 IO 库中是用于描述文件的结构,称为文件流。 FILE 结构在程序执行 fopen 等函数时会进行创建,并分配在堆中。FILE 结构定义在 libio.h 中,结构体名为_IO_FILE1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
/* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */
char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain; /* offset 0x68 (64bits) */
int _fileno;
int _blksize;
int _flags2;
_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
/* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
};
struct _IO_FILE_complete
{
struct _IO_FILE _file;
_IO_off64_t _offset;
/* Wide character stream stuff. */
struct _IO_codecvt *_codecvt;
struct _IO_wide_data *_wide_data;
struct _IO_FILE *_freeres_list;
void *_freeres_buf;
void *__pad1;
void *__pad2;
void *__pad3;
void *__pad4;
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
/* Make sure we don't get into trouble again. */
char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
};
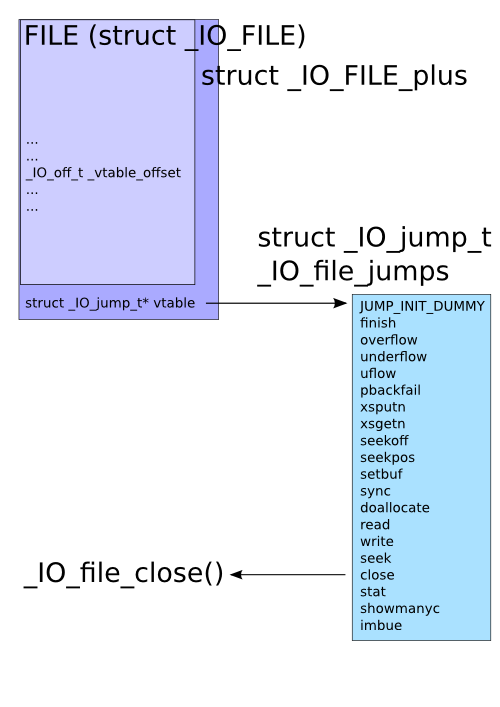
_IO_FILE_plus各项偏移如下:
1 | _IO_FILE_plus = { |
进程中的_IO_FILE结构会通过其结构体中struct _IO_FILE *_chain域进行链接,_IO_FILE_plus包含了结构体_IO_FILE和一个指向虚表的指针
1 | extern struct _IO_FILE_plus *_IO_list_all; |
_IO_list_all是一个指向_IO_FILE_plus结构体的指针,vtables是一个指向 IO_jump_t(虚表)的指针, IO_jump_t 中保存了一些函数指针,一系列标准 IO 函数执行时会调用这些函数指针
1 | struct _IO_jump_t |
下面是调用流程
0x01 为什么unsortedbin中的chunk会变成smallbin chunk,以及unsortedbin attack的说明
glibc分配chunk的过程如下
获取分配区的锁,为了防止多个线程同时访问同一个分配区,在进行分配之前需要取得分配区域的锁。线程先查看线程私有实例中是否已经存在一个分配区,如果存在尝试对该分配区加锁,如果加锁成功,使用该分配区分配内存,否则,该线程搜索分配区循环链表试图获得一个空闲(没有加锁)的分配区。如果所有的分配区都已经加锁,那么ptmalloc会开辟一个新的分配区,把该分配区加入到全局分配区循环链表和线程的私有实例中并加锁,然后使用该分配区进行分配操作。开辟出来的新分配区一定为非主分配区,因为主分配区是从父进程那里继承来的。开辟非主分配区时会调用mmap()创建一个sub-heap,并设置好top chunk。
将用户的请求大小转换为实际需要分配的chunk空间大小。
判断所需分配chunk的大小是否满足chunk_size <= max_fast,如果是的话,则转下一步,否则跳到第5步。
首先尝试在fast bins中取一个所需大小的chunk分配给用户。如果可以找到,则
分配结束。否则转到下一步。判断所需大小是否处在small bins中,即判断chunk_size < 512B是否成立。如果chunk大小处在small bins中,则转下一步,否则转到第7步。
根据所需分配的chunk的大小,找到具体所在的某个small bin,从该bin的尾部摘取一个恰好满足大小的chunk。若成功,则分配结束,否则,转到下一步。
到了这一步,说明需要分配的是一块大的内存,或者small bins中找不到合适的 chunk。于是,ptmalloc首先会遍历fast bins中的chunk,将相邻的chunk进行合并,并链接到unsorted bin中。然后遍历unsorted bin中的chunk,如果unsorted bin只有一个chunk,并且这个chunk在上次分配时被使用过,并且所需分配的chunk大小属于small bins,并且chunk的大小大于等于需要分配的大小,这种情况下就直接将该chunk进行切割,
分配结束,否则将根据chunk的空间大小将其放入small bins或是large bins中,遍历完成后,转入下一步。到了这一步,说明需要分配的是一块大的内存,或者small bins和unsorted bin中都找不到合适的 chunk,并且fast bins和unsorted bin中所有的chunk都清除干净了。从large bins中按照“smallest-first,best-fit”原则,找一个合适的 chunk,从中划分一块所需大小的chunk,并将剩下的部分链接回到bins中。若操作成功,则分配结束,否则转到下一步。
如果搜索fast bins和bins都没有找到合适的chunk,那么就需要操作top chunk来进行分配了。判断top chunk大小是否满足所需chunk的大小,如果是,则从top chunk中分出一块来。否则转到下一步。
到了这一步,说明top chunk也不能满足分配要求,所以,于是就有了两个选择: 如果是主分配区,调用sbrk(),增加top chunk大小;如果是非主分配区,调用mmap来分配一个新的sub-heap,增加top chunk大小;或者使用mmap()来直接分配。在这里,需要依靠chunk的大小来决定到底使用哪种方法。判断所需分配的chunk大小是否大于等于 mmap分配阈值,如果是的话,则转下一步,调用mmap分配,否则跳到第12步,增加top chunk 的大小。
使用mmap系统调用为程序的内存空间映射一块chunk_size align 4kB大小的空间。 然后将内存指针返回给用户。
判断是否为第一次调用malloc,若是主分配区,则需要进行一次初始化工作,分配一块大小为(chunk_size + 128KB) align 4KB大小的空间作为初始的heap。若已经初始化过了,主分配区则调用sbrk()增加heap空间,分主分配区则在top chunk中切割出一个chunk,使之满足分配需求,并将内存指针返回给用户。
在第7步,四个判断条件如下:
1 | victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk //取unsortedbin的最后一个chunk |
因为通过溢出,已经将unsortedbin chunk的bk覆盖为了_IO_list_all-0x10,而不是 unsorted_chunks (av),所以这条件不成立,之后是一个解引用:
1 | /* remove from unsorted list */ |
上述代码是unsortedbin attack的关键,覆盖unsortedbin chunk的bk时,也将fd覆盖为了垃圾数据,此时glibc判断unsortedbin中不止有一个freechunk,就将其解引用,此时指针_IO_list_all就指向了main_arena结构体中top对应的地址,即main_arena+88也就是unsorted bin头的地址,unsortedbin attack完成。
下面说一下为什么我们修改unsortedbin chunk的大小为0x61后,再次堆申请操作后,该chunk被链接到smallbin中。
在上面unsortedbin chunk解引用后:
1 | /* place chunk in bin */ |
这个size是unsortedbin chunk的大小,上面的分配都失败后,glibc会把unsortedbin中的chunk插入到smallbins或者largebins。
所以修改unsortedbin chunk的大小为0x61后,再次堆申请操作后,该chunk被链接到smallbin中。
0x02 为什么要让topchunk以brk的方式扩容
malloc小于128k的内存,使用brk分配内存,将heap_base往高地址推(只分配虚拟空间,不对应物理内存(因此没有初始化),第一次读/写数据时,引起内核缺页中断,内核才分配对应的物理内存,然后虚拟地址空间建立映射关系)。
malloc大于128k的内存,使用mmap分配内存,在堆和栈之间找一块空闲内存分配(对应独立内存,而且初始化为0)
为了方便对内存的读写,所以要让topchunk以brk的方式扩容
0x03 为什么chunk中会泄露libc和chunk的地址
由于largebin的链表中每个bin大小不一定相同,所以fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize记录了自己前一个和后一个与自己不同大小的bin的地址(只会记录同一链表上的关系,如果链表上只有一个bin的话则其两个nextsize都指向自己),所以会泄露heap地址。
fd,bk中泄露的是main_arean的地址
0x04 House of Orange程序分析
通过分析程序,可以总结有两个结构体
1 | struct house{ |
当程序执行完一次build函数时,堆中的结构如下
1 | +------------+ |
upgrade函数存在溢出,修改name的内容,进而溢出修改topchunk的数据
0x05 利用过程FSOP(File Stream Oriented Programming)
利用的触发点
我们修改了unsortedbin chunk的fd和bk,所以malloc时会出错
1 | if (__builtin_expect (victim->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0)|| __builtin_expect (victim->size > av->system_mem, 0)) |
函数调用链为:malloc_printerr->__libc_message->abort->_IO_flush_all_lockp
最后_IO_flush_all_lockp会调用vtable中的_IO_OVERFLOW函数,调用关系如下:
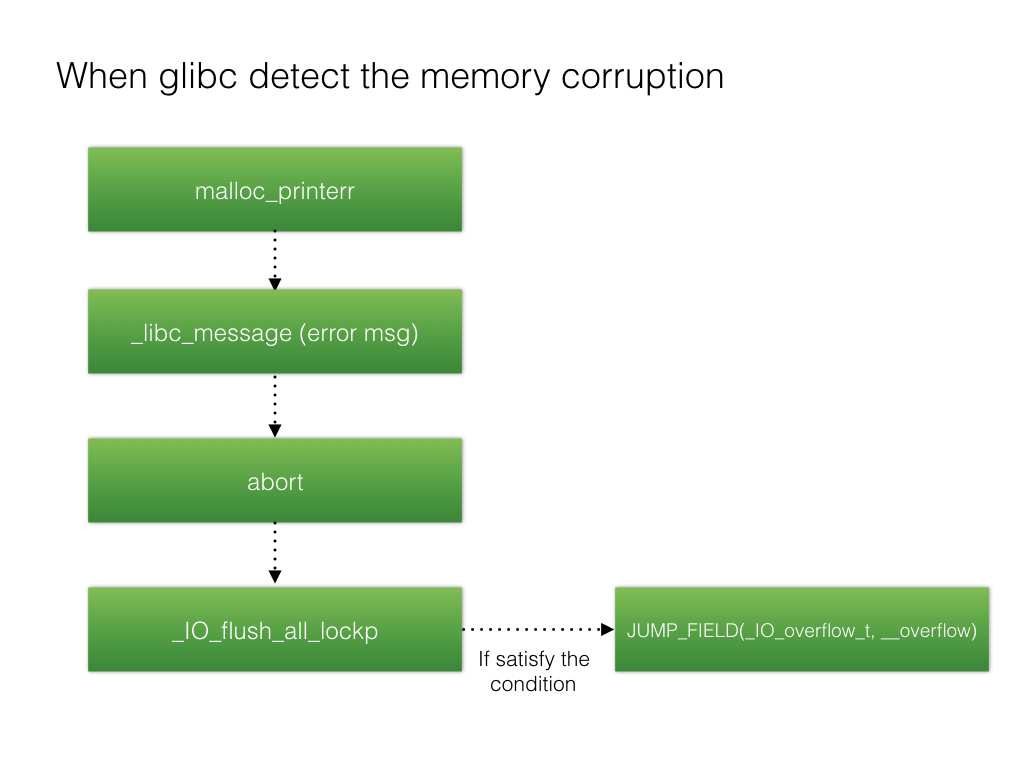
所以最终目的是修改vtable中的_IO_OVERFLOW为system
利用条件
1 | int _IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock) |
观察_IO_flush_all_lockp可以发现,要想成功调用_IO_OVERFLOW需要一些条件:
- fp->_mode <= 0
fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base
或
_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
- fp->_mode > 0
- fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base
第一种利用条件比较好构造,因此尝试用第一种
利用过程
- 获得一个unsortedbin。通过0x01中关于glibc分配chunk过程的内容,我们知道,当申请内存大小大于topchunk的大小时,程序会调用
sysmalloc来向系统申请更多的空间,具体分为sbrk()和mmap(),当申请的内存小于mmap_threshold(128*1024Bytes)时,会调用sbrk()申请内存,在原有堆上进行扩容。同时sysmalloc会调用_int_free(),释放原有的topchunk到unsortedbin。 通过unsortedbin attack将
_IO_list_all指针指向main_arena+88,即将main_arena结构体中top对应的地址,下为封装main_arena信息的结构体1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39struct malloc_state
{
/* Serialize access. */
mutex_t mutex;
/* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
int flags;
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top;//此地址将被写入_IO_list_all
/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
/* Bitmap of bins */
unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
/* Linked list */
struct malloc_state *next;
/* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized
by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
struct malloc_state *next_free;
/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on
the free list. Access to this field is serialized by
free_list_lock in arena.c. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;
/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
};
glibc将
main_arena+88当成了一个IO_FILE_plus结构体,发现一些if不满足,通过struct _IO_FILE *_chain寻找下一下IO_FILE_plus文件流struct _IO_FILE *_chain在_IO_FILE_plus结构体偏移0x68处,而main_arena+88(unsorted bin头的地址) 偏移0x68处正好是存储0x60 freechunk的smallbin的bk,而里面的内容时可以控制的1
2
3
4
5
6
7+0x00 [ top | last_remainder ]
+0x10 [ unsorted bin fd | unsorted bin bk ]
+0x20 [ smallbin 0x20 fd | smallbin 0x20 bk ]
+0x30 [ smallbin 0x30 fd | smallbin 0x30 bk ]
+0x40 [ smallbin 0x40 fd | smallbin 0x40 bk ]
+0x50 [ smallbin 0x50 fd | smallbin 0x50 bk ]
+0x60 [ smallbin 0x60 fd | smallbin 0x60 bk ]我们可以将原来是topchunk,被glibc释放掉变成unsortedbin chunk的chunksize改为0x61,通过标题0x01可知,该chunk会被加入到smallbins中,该smallbin的fd,bk都会变成该chunk的地址。当前
_IO_list_all指向的内容不满足执行_IO_OVERFLOW,进而通过fp->_chain寻找下一个_IO_FILE时,就会根据smallbin的bk寻找到0x60smallbin中的chunk。之后回调用虚表函数,我们将vtable指针修改为伪造的
_IO_FILE_pluschunk的后面的堆内存,将_IO_OVERFLOW修改为system,即成功劫持的控制流
0x06 EXP
1 | #/usr/bin/env python |
0x07 REFFERENCE
[理解 glibc malloc:malloc() 与 free() 原理图解]https://blog.csdn.net/maokelong95/article/details/52006379